Integrating AI in the Classroom
Guidance that support districts and charters in understanding and implementing instructional AI tools
To fully realize Generative AI’s potential in education, school districts and charter schools must ensure that educational and technological standards are met, thereby facilitating the use of Generative AI tools to augment educational experiences.
State and local policymakers and academic leaders should establish an equitable framework supporting comprehensive policies catering to all students’ diverse needs and capabilities. This approach will ensure the safe and effective use of AI tools in learning environments, preparing students for future challenges and opportunities.
Protecting Student Data with Generative AI Classroom Integration
Integrating Generative AI into K-12 education presents a transformative opportunity to enhance learning experiences and outcomes. However, it necessitates a meticulous approach to protecting student data, ensuring privacy, and maintaining compliance with legal frameworks such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA). School Districts and Charter Schools must prioritize establishing robust data governance policies with precise data collection, storage, access, and sharing protocols. Implementing these tools should be accompanied by rigorous security measures, including encryption and secure authentication, to safeguard against unauthorized access to sensitive information. Furthermore, transparency with students and parents about using Generative AI and the data it generates is crucial.
This involves providing accessible information on how data is used to support educational goals and how privacy is protected. By thoughtfully integrating technologies within a framework of strong data protection practices, academic institutions can unlock the potential of Generative AI to personalize learning while simultaneously upholding the trust and confidence of the educational community in the digital age. The Delaware Department of Technology and Information provides terms and conditions for cloud services and student data usage. This documentation needs to be recorded and signed when contracting with vendors.
Ensuring Ethical AI Use with AI Classroom Integration
Educators must prioritize digital citizenship and media literacy when integrating Generative AI into the classroom to empower students with essential skills for navigating the digital world. Digital Citizenship encompasses diverse skills, fostering an understanding ofappropriate, responsible, ethical, and healthy behavior. Media literacy involves accessing, evaluating, creating, and taking action with various forms of communication, including AI-generated responses (AIFWD, 2023).
Promoting Equity with Generative AI Classroom Integration
Adopting Generative AI in education necessitates focusing on ethics, equity, and digital literacy. This involves addressing potential biases in these systems, ensuring data privacy, and promoting an inclusive learning environment that benefits all students. Educational leaders must establish policies and practices reflecting these values, ensuring AI tools are used ethically, equitably, and effectively.
Enhancing Learning with Generative AI Classroom Integration
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize learning by providing access to personalized and immersive educational experiences.
Examples include using augmented reality (AR) for interactive learning sessions and employing chatbots for tutoring and support. These applications engage students in novel ways and support diverse learning styles and needs, making education more accessible and practical.
Integrating Generative AI allows educators to engage students in deep and meaningful learning, promoting high levels of creativity and critical thinking skills. Our role as educators is to educate our students, teaching them how to use Generative AI appropriately to enhance their learning, creativity, and demonstration of standard mastery.
Best Practices for Integrating Generative AI
- When selecting a Generative AI tool, carefully review the age restrictions, privacy, and data collection policies before implementing them in the classroom.
- Participate in a classroom discussion on plagiarism and establish guidelines forGenerative AI citations. (Citation resources: MLA Style – Generative AI , APA Style – ChatGPT, and Chicago Style – Generative AI; OpenAI has a “Get Citation” feature that creates a current citation)
- Be clear about how and when students are expected to use or not use AI.
- Permissive: Students freely utilize AI tools to assist in assignments, such as generating ideas, proofreading, or organizing content.
- Moderate: Students may use AI tools for specific parts of the assignment, such as brainstorming or initial research, but core content and conclusions are original.
- Restrictive: AI tools are prohibited for the assignment, and all work must be author’s original creation (OpenAI, 2023).
- Avoid using AI detection tools as they are proven unreliable, often resulting in false positives (e.g., Checking the Google version history of the document to see if paragraphs have been added in one keystroke).
- Provide instruction on how students can be critical consumers of Generative AI, evaluating responses to see if they meet their needs and verifying facts, figures, quotes, and data using reliable sources.
- Consider how Generative AI may be used as a thought partner for students as a brainstorming tool or to provide feedback.
- Ensure equity by making Generative AI tools available to all students, considering that some may and some may not have access outside of school if an assignment permits use.
- Provide a blended learning experience integrating technology with discussions, hands-on learning, and project-based assignments and assessments.
AI and the SAMR Model
The SAMR model, developed by Dr. Ruben Puentedura, provides a framework for incorporating technology into education and categorizes technology integration into four levels: Substitution, Augmentation, Modification, and Redefinition.
Generative AI and Student Learning
As K-12 education systems increasingly integrate Generative AI into the learning environment, it is imperative to harness its transformative potential responsibly and effectively. This guidance aims to illuminate Generative AI’s benefits in enhancing student well-being and improving learning outcomes, as well as the associated risks and strategies for their mitigation.
Benefits
Personalized Content and Review: AI can help generate personalized study materials, summaries, quizzes, and visual aids, help students (including those with disabilities) access and develop tailored resources to meet their specific needs, and help students organize thoughts and review content.
Aiding Creativity: Students can harness generative AI as a tool to spark creativity across diverse subjects, including writing, visual arts, and music composition. AI can suggest novel concepts or generate artwork or musical sequences to build upon.
Tutoring: AI technologies have the potential to democratize one-to-one tutoring and support, especially for students with financial or geographic constraints. Virtual teaching assistants powered by AI can provide round-the-clock support, help with homework, and supplement classroom instruction.
Critical Thinking and Future Skills: Students who learn about how AI works are better prepared for future careers in a wide range of industries. They can develop computational thinking skills to break down complex problems, analyze data critically, and evaluate the effectiveness of solutions.
Risks
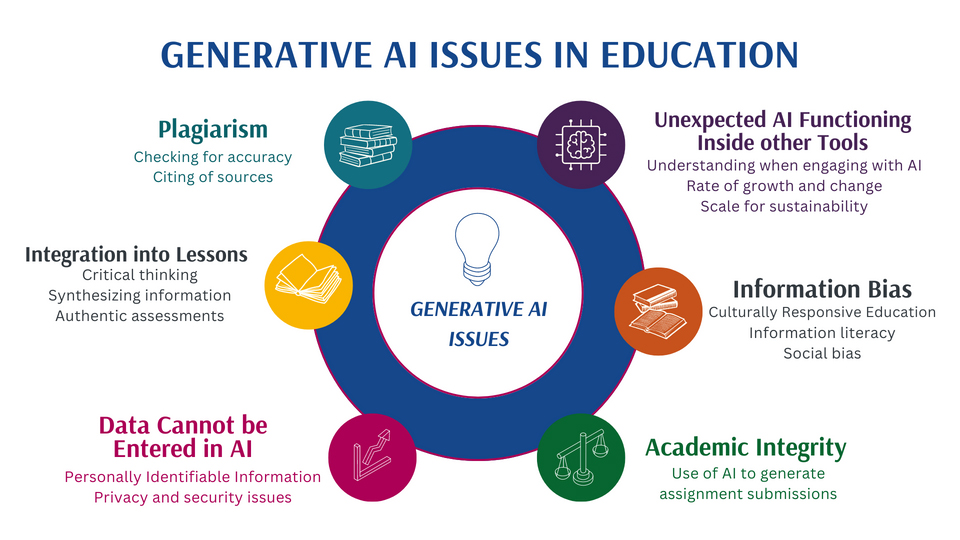
Plagiarism and cheating can occur when students copy from generative AI tools without approval or adequate documentation and submit AI-Generated work as their original work.
Misinformation can be produced by Generative AI tools, leading to widespread misconceptions.
Bullying and harassment by using AI tools to manipulate media in order to impersonate others can have severe consequences for students’ well-being.
Overreliance on AI models can lead to undercutting the learning process and abandoning human discretion and oversight. Important nuances and context can be overlooked andaccepted. People may overly trust AI outputs, especially when AI is seen as having human-like characteristics.
Unequal access to AI tools worsens the digital divide between students with independent and readily available access at home or on personal devices and students dependent on school or community resources.
Risk Mitigation
In addition to being clear about when and how AI tools may be used to complete assignments, teachers can restructure assignments to reduce opportunities for plagiarism and decrease the benefit of AI tools. This may include evaluating the artifact developmentprocess rather than just the final artifact and requiring personal context, original arguments,or original data collection.
Students should learn how to critically evaluate all AI-generated content for misinformationor manipulation and be taught about responsible development and sharing of content.
Staff and students should be taught how to properly cite and acknowledge the use of AI where applicable.
If an assignment permits the use of AI tools, the tools must be made available to all students, considering that some may already have access to such resources outside of school.